Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (30): 4838-4844.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.30.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mechanical strength and bacterial inhibition of glass ionomer cements
Liu Li-xia1, Chen Lin2
- 1Department of Stomatology, Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
2Jiamusi Jinjue Institute for Dentistry, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-06-02Online:2014-07-16Published:2014-08-08 -
Contact:Chen Lin, Master, Attending physician, Jiamusi Jinjue Institute for Dentistry, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Li-xia, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Li-xia, Chen Lin . Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mechanical strength and bacterial inhibition of glass ionomer cements[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(30): 4838-4844.
share this article
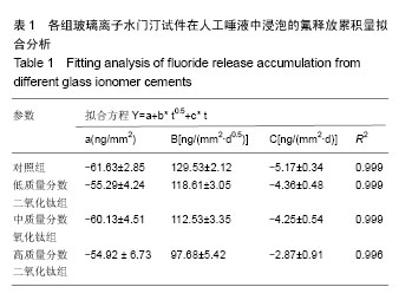
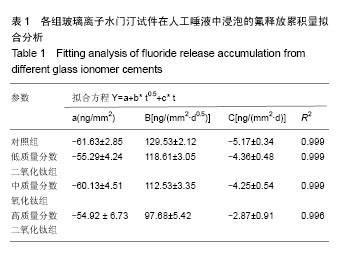
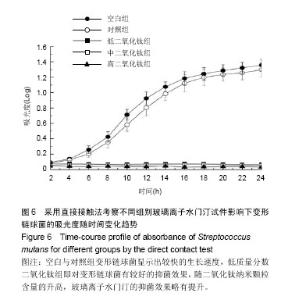
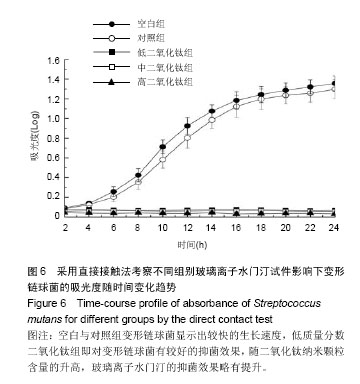
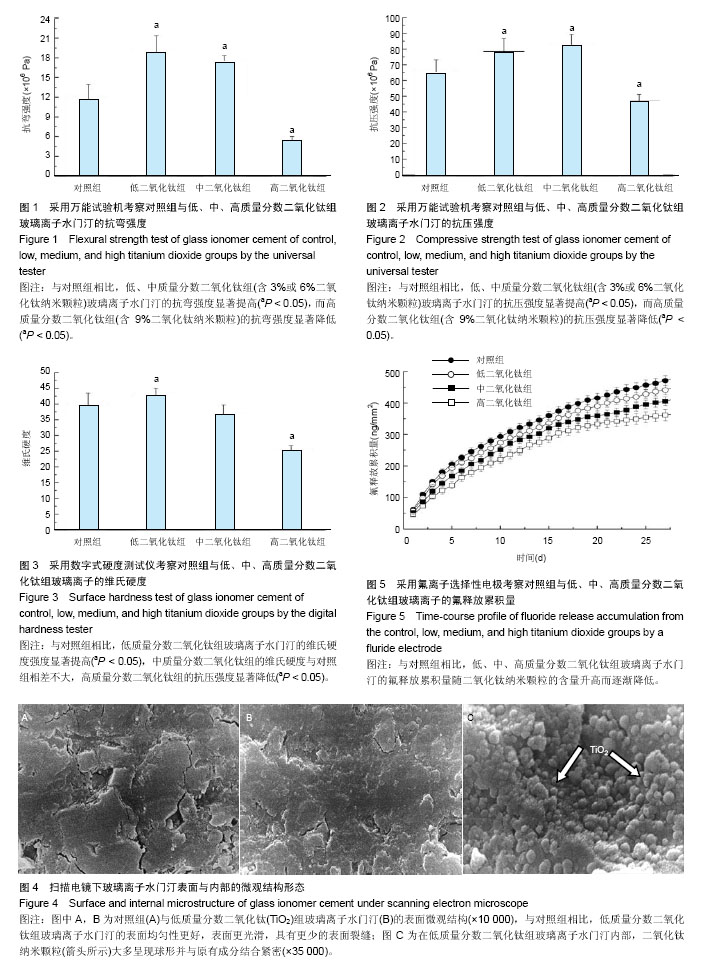
2.1 各组玻璃离子水门汀试件的抗弯强度 图1显示对照组玻璃离子水门汀与低、中、高质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的抗弯强度。在不加入二氧化钛纳米颗粒时,对照组玻璃离子水门汀的抗弯强度仅为11.59×106 Pa。少量二氧化钛纳米颗粒(3%)的加入即可显著提高Fuji II的抗弯强度,达到18.67×106 Pa。当二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量继续增加时,Fuji II的抗弯强度逐渐下降,从6%二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量时的17.24×106 Pa,迅速下降到9%二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量时的5.32×106 Pa。除低质量分数二氧化钛组与加入6%二氧化钛纳米颗粒两组以外,其他的组间两两比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.2 各组玻璃离子水门汀试件的抗压强度 图2显示对照组与低、中、高质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的抗压强度,如图可知对照组玻璃离子水门汀的抗压强度随二氧化钛纳米颗粒的含量增加呈现先升高后降低的趋势。对照组玻璃离子水门汀的抗压强度由原始的65.04×106 Pa,提高到低质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的89.35× 106 Pa。对中质量分数二氧化钛组,玻璃离子水门汀抗压强度略微降至82.23×106 Pa。当二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量进一步提高时(高质量分数二氧化钛组),玻璃离子水门汀抗压强度显著下降,仅为46.77×106 Pa。与抗弯强度的统计学分析结果类似,除低质量分数二氧化钛组与中质量分数二氧化钛组两组间以外,其他的组间两两比较差异均有显著的显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3 各组玻璃离子水门汀试件的表面硬度 图3显示对照组与低、中、高质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的表面维氏硬度,如图可知少量二氧化钛纳米颗粒(3%)的加入对玻璃离子水门汀的表面硬度有一定的提升效果。对低质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀,其维氏硬度由对照组的38.92略微增加到42.35。中质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的维氏硬度与对照组相差不大,约为36.44。当二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量进一步提升时(高质量分数二氧化钛组),玻璃离子水门汀的维氏硬度显著下降,仅为25.03。通过统计学分析发现,低质量分数二氧化钛组和高质量分数二氧化钛组与对照组的维氏硬度差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 对照组与低质量分数二氧化钛组的表面结构与内部微观形态 图4A,B显示对照组与低质量分数二氧化钛组通过SEM扫描电镜得到的的表面结构图。如图可知,与对照组相比,低质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀表面均匀性更好,表面更加光滑,同时具有更少的表面裂缝。图4C显示低质量分数二氧化钛组玻璃离子水门汀的内部微观形态,如图可知二氧化钛纳米颗粒与玻璃离子水门汀原有成分结合紧密,二氧化钛纳米颗粒大多呈现球形并均匀分布在玻璃离子水门汀试件内部。 2.5 各组玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量的动态变化趋势与拟合分析 图5显示不同组别玻璃离子水门汀试件的氟释放累积量随时间变化趋势,如图可知各组玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放累积量随时间变化趋势均表现为平滑递增曲线,而氟释放累积量随二氧化钛纳米颗粒的含量升高而逐渐降低,在第28天时,对照组玻璃离子水门汀达到478.52 ng/mm2的氟释放累积量,随后依次为低质量分数二氧化钛组(449.87 ng/mm2),中质量分数二氧化钛组(412.51 ng/mm2)和高质量分数二氧化钛组(364.17 ng/mm2)。采用拟合方程 Y=a+b*t0.5+c* t对4组玻璃离子水门汀氟释放累积量进行非线性回归分析。表1显示拟合方程的重要参数值和相关系数R2。如表可知,该方程可较好模拟各组玻璃离子水门汀试件的氟释放过程,对对照组、低质量分数二氧化钛组和中质量分数二氧化钛组的相关系数均为0.999,高质量分数二氧化钛组也达到了0.996。 2.6 各组玻璃离子水门汀试件对变形链球菌的抗菌性能 图6显示不同组别玻璃离子水门汀试件影响下变形链球菌的吸光度随时间变化趋势。如图可知,对空白和对照组玻璃离子水门汀试样,变形链球菌呈现一个较快的生长速度,在第24小时时,吸光度分别达到了1.36和1.30,未表现出抑菌效果。而对各实验组玻璃离子水门汀试样而言,少量比例二氧化钛纳米颗粒的加入即可产生明显的抑菌效果,对低质量分数二氧化钛组,在第24小时时,吸光度仅为0.10。当二氧化钛纳米颗粒含量继续增加时, 玻璃离子水门汀试样的抑菌效果略有提升,对中质量分数二氧化钛组和高质量分数二氧化钛组,第24小时时的吸光度分别为0.06和0.03。"
| [1] 裴壮敏.玻璃离子水门汀用于口腔正畸的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(26):306-307. [2] 廖伟,周年苟,扈祚文,等.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验[J].中国组织工程实验与临床康复,2011,15(8):1467-1470. [3] Balamungan A, Baiossier G, Lanrent-Maquifi D, et al. An in vitro biological and antibacterial study oll a sollel derived silver-incerporated biogless system. Dent Mater. 2008; 24(10):1343-1351. [4] Arita K, Lucas ME, Nishino M. The effect of adding hydroxyapatite on the flexural strength of glass ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2003;22(2):126-136. [5] 赵昱,苏葆辉,冉均国,等.乙酸处理对玻璃离子水门汀性能的影响[J].硅酸盐通报,2013,32(2):304-308. [6] Smith DC. Development of glass-ionomer cement systems. Biomaterials. 1998;19:467-478. [7] Dowling AH, Stamboulis A, Fleming GJ. The influence of montmorillonite clay reinforcement on the performance of a glass ionomer restorative. J Dent. 2006;34:802-810. [8] Nakajima N, Watkins JH, Arita K, et al. Mechanical properties of glass ionomers under static and dynamic loading. Dent Mater. 1996;12:30-37. [9] 刘莉霞,陈琳.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀的氟释放行为与溶解性[J].中国组织工程实验,2014,18(16):2480-2486. [10] 陈娜,刘聪,李行懿.不同类型玻璃离子水门汀氟释放能力的比较分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(10):64-66. [11] 董波,刘文斌,李晶晶,等.纳米纤维素晶须对新型玻璃离子水门汀增韧作用的影响[J].中国体视学与图像分析,2013,18(4):361- 366. [12] 董波,徐志媛,刘文斌,等.纳米纤维素晶须对玻璃离子水门汀的性能影响[J].中国体视学与图像分析,2013,18(1):23-28. [13] 冯瑶,冯思聪,王建平,等.玻璃离子水门汀加入改良纳米羟基磷灰石后的性能[J].中国组织工程实验,2013,17(42):7382- 7388. [14] Moshaverinia A, Ansari S, Moshaverinia M, et al. Effects of incorporation of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite nanobioceramics into conventional glass ionomer cements (GIC). Acta Biomaterialia, 2008;4:432-440. [15] Prentice LH, Tyas MJ, Burrow MF. The effect of ytterbium fluoride and barium sulphate nano particles on the reactivity and strength of a glass-ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:746-751. [16] Moshaverinia A, Ansari S, Movasaghi Z, et al. Modification of conventional glass-ionomer cements with N-vinylpyrrolidone containing polyacids, nano-hydroxy and fluoroapatite to improve mechanical properties. Dent Mater. 2008;24: 1381-1390. [17] Tllrklln LS, Turkan M. Long-term antibacterial effects and physical properties of a chlorhexidine-containing glass ionomer cement. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2008;20(1):29-45. [18] Xia Y, Zhang F, Xie H, et al. Nano particle-reinforced resinbased dental composites. J Dent. 2008;36:450-455. [19] 尹雯娟,叶慧铭,侯雅蓉,等.玻璃离子水门汀调拌过程中常见问题分析[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(22):3784-3784. [20] 曹院琴,李永祥.3种玻璃离子水门汀氟释放能力的体外实验[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(2):116-118. [21] 张海英,吕松,侯本祥.四种玻璃离子充填材料释氟性与溶解性的实验[J].北京口腔医学,2011,19(5):260-262. [22] Al Zraikat H, Palamara JE, Messer HH, et al. The incorporation of casein phosphopeptideamorphous calcium phosphate into a glass ionomer cement. Dent Mater. 2011; 27:235-243. [23] Kao EC, Culbertson BM, Xie D. Preparation of glass ionomer cement using N-acryloyl-substituted amino acid monomers-evaluation of physical properties. Dent Mater. 1996;12:44-51. [24] Tanumiharja M, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ. Microtensile bond strengths of glass ionomer (polyalkenoate) cements to dentine using four conditioners. J Dent. 2000;28:361-366. [25] Tsuang YH, Sun JS, Huang YC, et al. Studies of photokilling of bacteria using titanium dioxide nano particles. Artificial Organs. 2008;32:167-174. [26] Chan WD, Yang L, Wang W, et al. Fluoride release from dental cements and composites: a mechanistic study. Dent Mater,2006;22(4):366-373. [27] Verbeeck RM, deMoor RJ, Van Even DF, et al. The short-term fluoride release of a hand-mixed vs. cap sulated system of a restorative glass-ionomer cement. J Dent Res. 1993;72: 577-581. [28] Choi JY, Lee HH, Kim HW. Bioactive sol-gel glass added ionomer cement for the regeneration of tooth structure. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(10):3287-3294. [29] Vermeersch G, Leloup G, Delmee M, et al. Antibacterial activity of glass-ionomer cements, compomers and resin composites: relationship between acidity and material setting phase. J Oral Rehabilit. 2005;32:368-374. [30] Nychka JA, Li D, Alexander B. In vitro bioactivity of 45S5 bioactive glass as a function of indentation load. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2008;1(3):243-251. [31] Butler KS, Casey BJ, Garbocauskas GV, et al. Assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticle effects in bacteria: Association, uptake, mutagenicity, co-mutagenicity and DNA repair inhibition. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014. [32] Makumire S, Chakravadhanula VS, Köllisch G, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of zinc peroxide (ZnO?) and titanium dioxide (TiO?) nanoparticles and their effects on DNA and protein integrity. Toxicol Lett. 2014;227(1):56-64. [33] Dasari TP, Hwang HM. Effect of humic acids and sunlight on the cytotoxicity of engineered zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles to a river bacterial assemblage. J Environ Sci (China). 2013;25(9):1925-1935. [34] Minetto D, Libralato G, Volpi Ghirardini A. Ecotoxicity of engineered TiO2 nanoparticles to saltwater organisms: an overview. Environ Int. 2014;66:18-27. [35] Kedziora A, Gerasymchuk Y, Sroka E, et al. Use of the materials based on partially reduced graphene-oxide with silver nanoparticle as bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent. Polim Med. 2013;43(3):129-134. [36] Binh CT, Tong T, Gaillard JF, et al. Common freshwater bacteria vary in their responses to short-term exposure to nano-TiO2. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2014;33(2):317-327. [37] Gartiser S, Flach F, Nickel C, et al. Behavior of nanoscale titanium dioxide in laboratory wastewater treatment plants according to OECD 303 A. Chemosphere. 2014;104:197-204. [38] Hammond SA, Carew AC, Helbing CC. Evaluation of the effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cultured Rana catesbeiana tailfin tissue. Front Genet. 2013;4:251. [39] Zhou L, Zhang Z, Xia S, et al. Effects of suspended titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cake layer formation in submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol. 2014;152:101-106. [40] Shokri M, Jodat A, Modirshahla N, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of chloramphenicol in an aqueous suspension of silver-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Technol. 2013; 34(9-12):1161-1166. [41] Patil MA, Parikh PA. Investigation on likely effects of Ag, TiO2, and ZnO nanoparticles on sewage treatment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;92(1):109-114. [42] Zhang J, Liu Y, Li Q, et al. Antifungal activity and mechanism of palladium-modified nitrogen-doped titanium oxide photocatalyst on agricultural pathogenic fungi Fusarium graminearum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(21): 10953-10959. [43] Frazier TP, Burklew CE, Zhang B. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles affect the growth and microRNA expression of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Funct Integr Genomics. 2014; 14(1):75-83. [44] Vatansever F, Ferraresi C, de Sousa MV, et al. Can biowarfare agents be defeated with light? Virulence. 2013; 4(8):796-825. [45] Shah N, Ul-Islam M, Khattak WA, et al. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: a multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;98(2):1585-1598. |
| [1] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [5] | Li Hui, Zhang Kun, Hao Yangquan, Feng Lei, Yang Zhi, Xu Peng, Lu Chao. Robot-assisted core decompression and bone grafting for ARCO II osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 547-551. |
| [6] | Hong Xiao, Luo Hong, Yang Ruonan. Comparison of dynamic hip screw and anti-rotation screw internal fixation and femoral neck system internal fixation in the treatment of Garden II-IV femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 583-587. |
| [7] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [8] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [9] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| [10] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [11] | Guo Sutong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Ren Tianhao, Xu Haitao, Wang Yulin, Feng Dehong. Finite element analysis of hip stress distribution at different hip abduction angles in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4265-4270. |
| [12] | Li Jiawei, Li Canran, He Yujie, Wu Chao, Jin Feng, Zhang Kai, Li Xiaohe. Digital measurement of femoral valgus angle and femoral posterior condyle angle in elderly people over 60 years old in northern China and comparison with young and middle-aged population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4291-4296. |
| [13] | Li Junran, Zhai Jingxiu, Zhao Hongbo, Wang Lei, Wang Hongrun, Liang Junsheng, Li Ligeng. Assistance of traction table for total hip arthroplasty through the direct anterior approach for treating femoral neck fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4312-4317. |
| [14] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Effect of distal tibial tuberosity-high tibial osteotomy on patellofemoral joint degeneration and patellar height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4367-4372. |
| [15] | Chen Bohao, He Qi, Yang Junzheng, Pan Zhaofeng, Xiao Jiacong, Li Miao, Li Shaocong, Zeng Jiaxu, Wang Haibin, Zheng Jia, Zhang Meng. Significance of Piezo1 protein in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4414-4420. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||